In internet jargon, all of these devices are called hosts or end systems.
Big picture
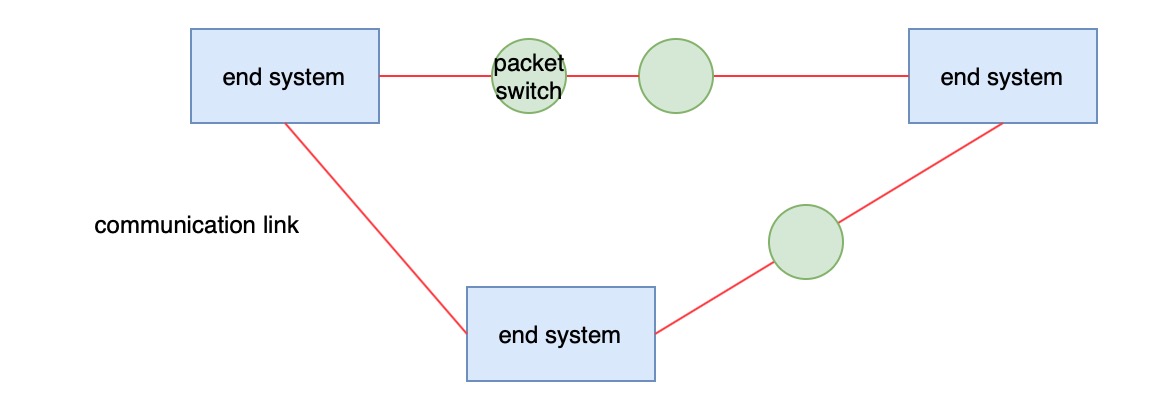
End systems are connected by a network of communication links and packet switches. Communication links are made of physical media, including coaxial cable, copper wire, optical fiber, and radio spectrum. Transmission rate is the measure, which is in bits/second. Packet switch is referred to routers and link-layer switches. link-layer switches are used in access networks, while routers are used in the network core.
Socket interface is set of rules that a program on an end system tells Internet how to deliver the data to the destination program.
Network protocal defines the format and the order of messages exchanged between two or more communicating entities, as well as the actions taken on the transmission and/or receipt of a message o other event.
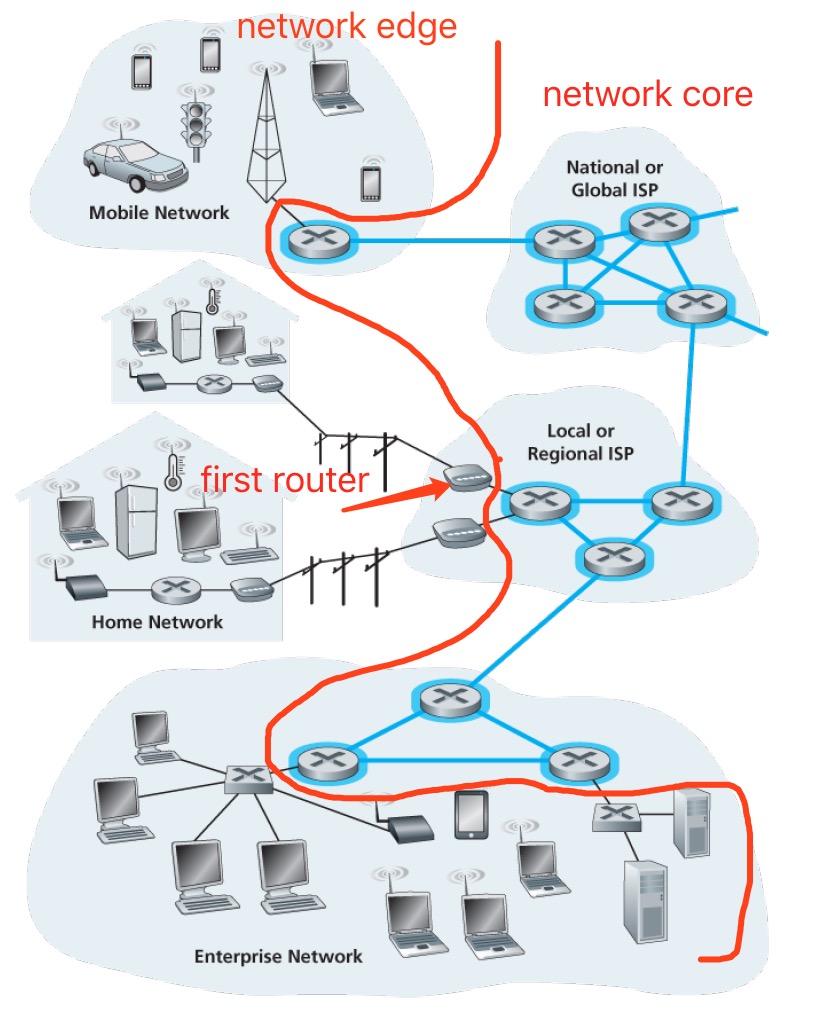
Network edge
applications and end systems.
Network is composed by network edge and network core. End system are also refferred to as hosts because they run application programs such as a Web browser program, a Web server program, an e-mail client program, or an e-mail server program. hosts and end system are exchangeable. hosts are sometimes divided into two categories: clients and servers. Mang servers are together in data center, such as Google.
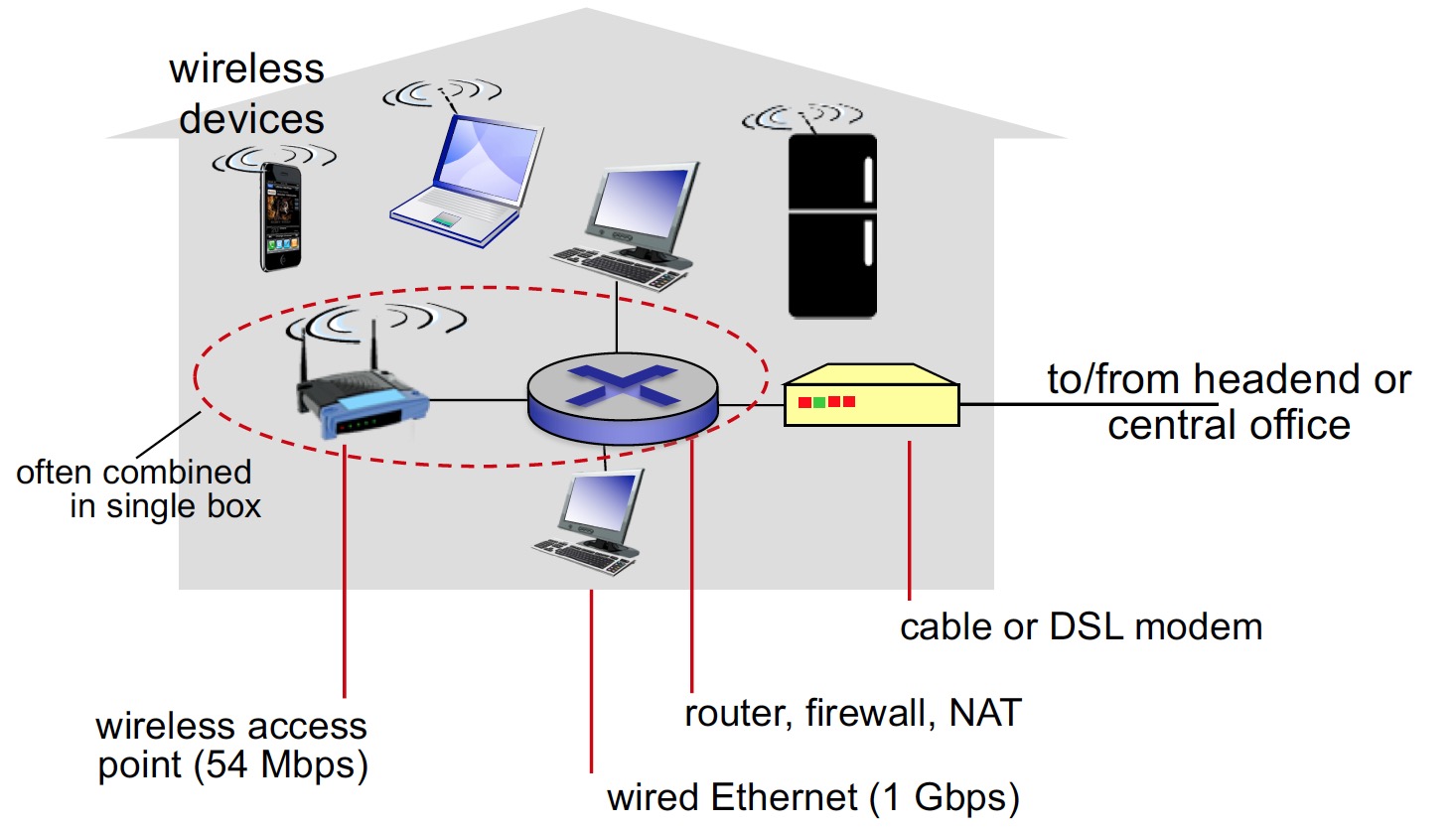
Access networks refers to the network that physically connects and end system to the first router(also known as “edge router”).
Home network access: DSL (digital subscriber line), cable, FFTH (fiber to the home, faster than others), Dial-up,Statellite.
Network core
The mesh of packet switches and links that interconnects the Internet’s end system.
Packet Switching**
transmission rate can’t be reserved, each packet transmitted at full link capacity, result in queue delay.
Most packet switches use store-forward transmission at the input to the links. Which means that the packet switch must recieve the entire packet before it can begin to transmit the first bit of the packet onto the outbound link.
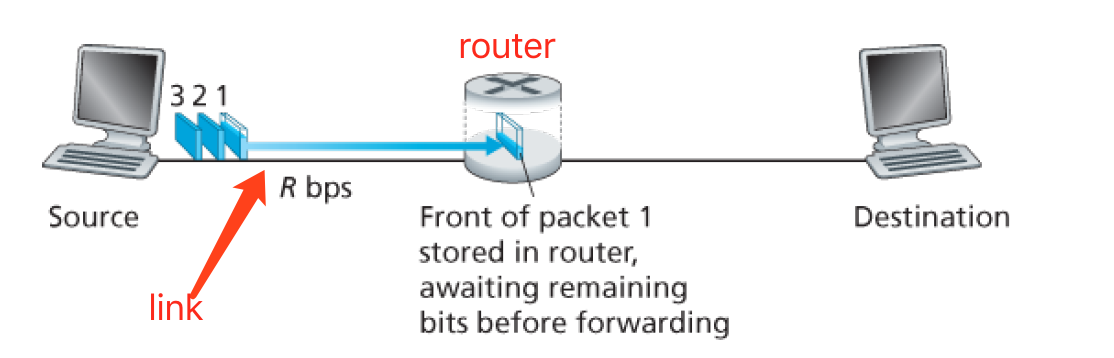
Whole process from source to destionation: hosts break application-layer essages into packet -> router push packet to link -> link propagates to destionation.
Each router has a forwarding table that maps destination addresses (or portions of the destination addresses) to that router’s outbound links. routing protocals are used to automatically set the forwarding tables.
Circuit Switching
a given transmission rate has been reserved, divided link capacity, need handshake to build connection before transmission.
Circuit switches require reservations while packet switches neither require reservations nor accepts them. Tradictional telephone call is circuit switching, and Internet is packet switching.
Two types:
- frequency-division multiplexing (FDM): continuous get divided bandwidth.
- time-division multiplexing (FDM): get full bandwidth in interval time.
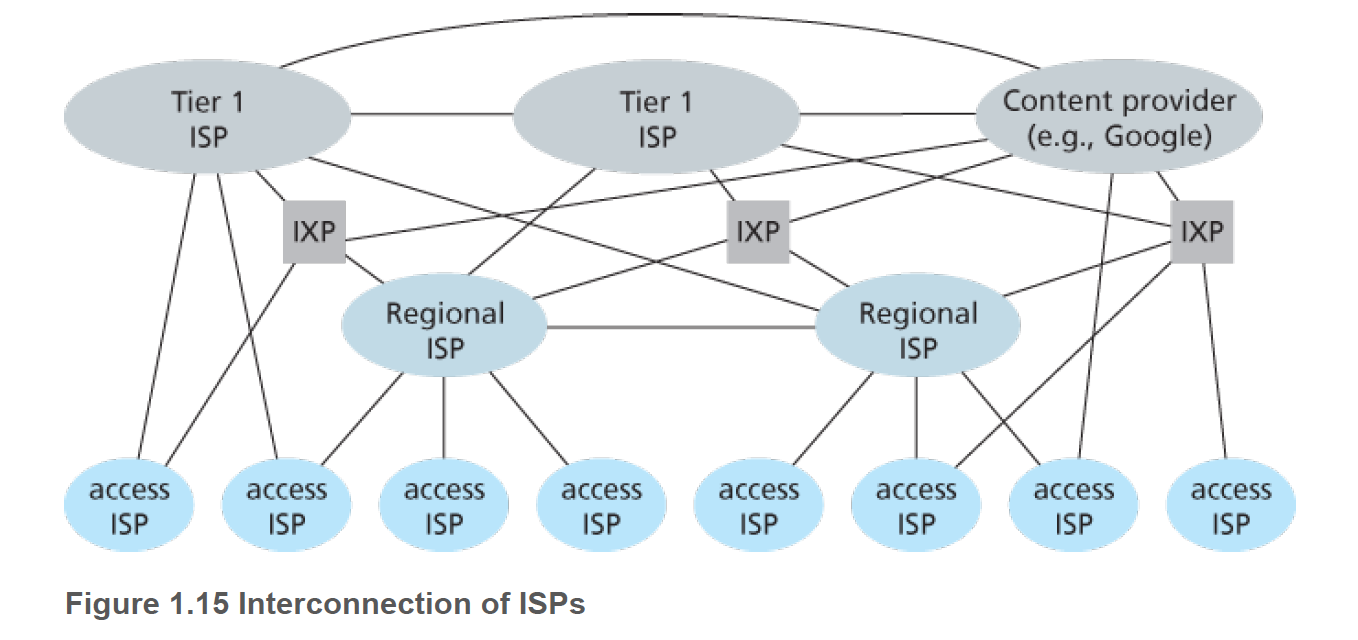
Internet structure
Internet structure is a network of Networks
ISP: End systems access the Internet through Internet Service Providers (ISPs).
IXP: Internet Exchange Point, link ISPs.
Access net: reginal net.
Reference material:
Book: Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach 7th edition, Jim Kurose & Keith Ross, Addison-Wesley.
Slides: University of Waterloo, ECE 456/656 (Computer Networks), 2020 spring term, Professor Zille Huma Kamal.