Background
Web browser, mail reader, DNS are employeed server-client architectures. Imaging file system is a server-client distributed system, then one server has heavy load and traffic jam. If file system is a P2P distributed system, then one large file is distributed as some parts on many peers. The most popular P2P file distribution protocol is BitTorrent.
Scalibility of P2P architectures
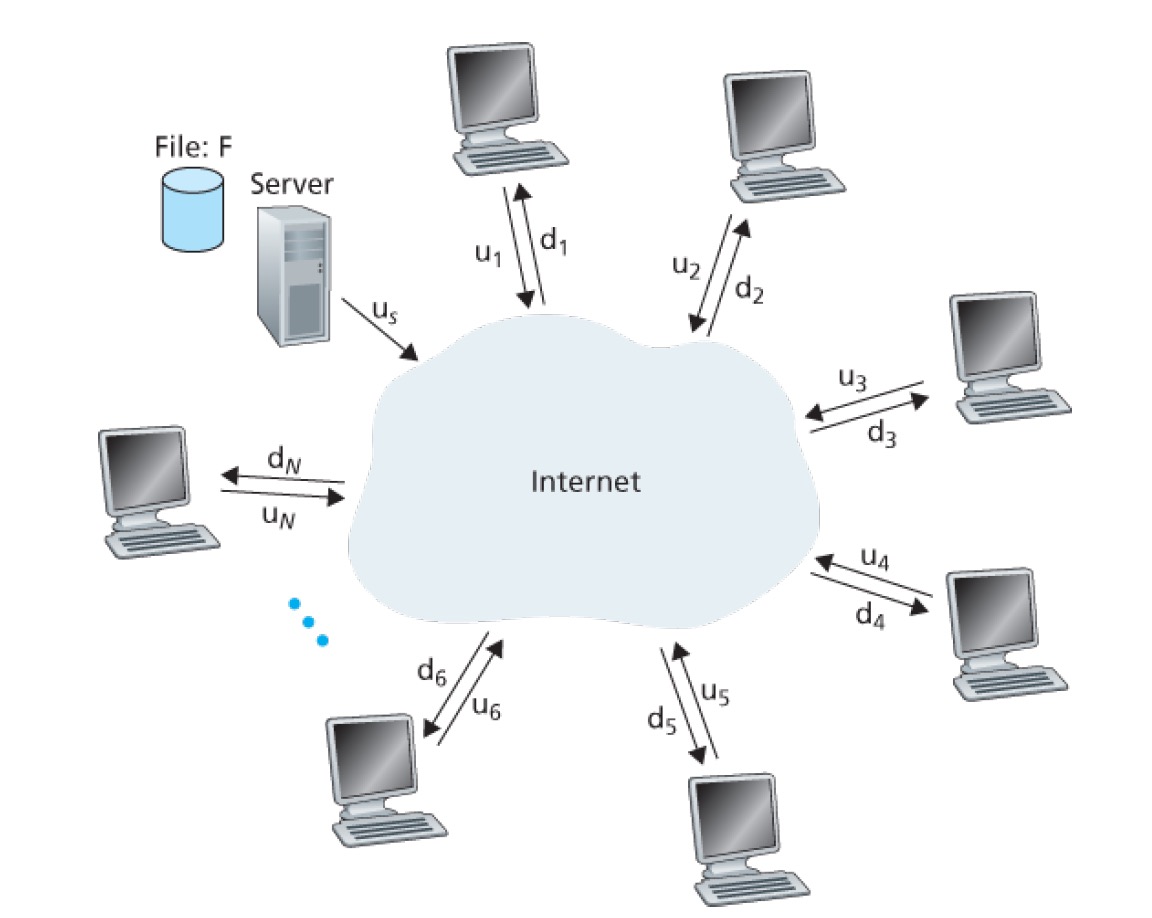
- us – upload rate of server
- ui – upload rate of ith peer
- dmin – minimum download rate of peers
- F – distributed file size
- N – number of peers
- Dcs – distributed time of client-server distributed architecture
- Dp2p – distributed time of P2P distributed architecture
- Distributed time: the time it takes to assign a copy of file to all N peers.
- the time of server uploading to each peer one copy of the file: NF/us
- the maximum time of download whole file from peers: F/dmin
Total time Dcs = max{NF/us, F/dmin}.
- the server must upload each bit of the file at least once into its access link. The minimum time: F/us
- the maximum time of download whole file from peers: F/dmin
- the total upload capacity of the system as a whole is equal to the upload rate of the server plus the upload rates of each of the individual peers, that is, Utotal=u
s+u1+ … + uN. The system must upload F bits to each of peers, then total bits is NF. The distribution time is NF/utotal
Total time DP2P >= max{us, F/dmin, NF/utotal}.
A peer can also distribute a file after receiving it from the server, this time consume is more complex.
BitTorrent Protocol
Torrent is a collection of peers. Each torrent has an infrastructure node called a tracker.
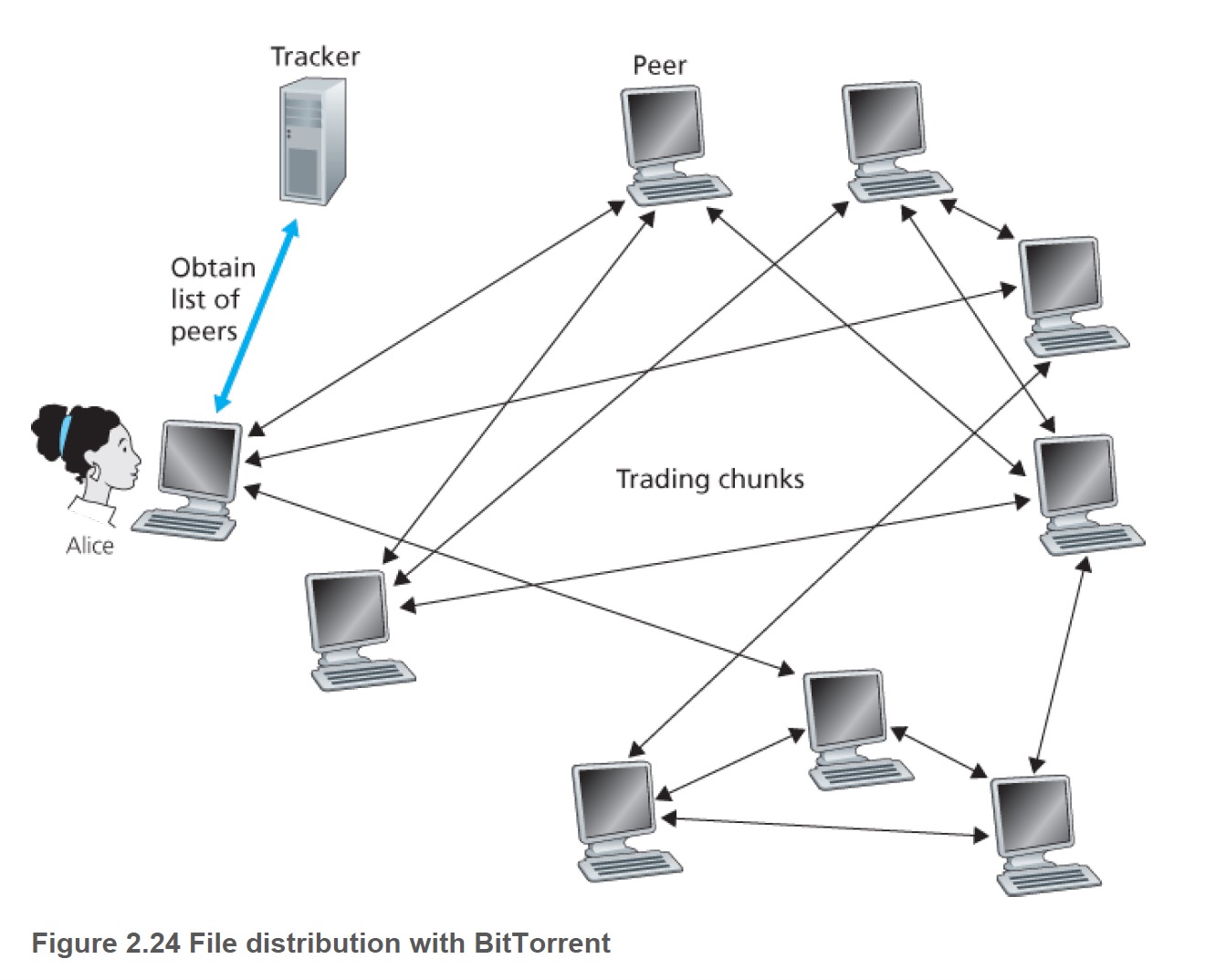
Explaination:
- Alice join the torrent, then register itself with tracker. The tracker selects a list of subset of the peers and sends Alice their IP addresses.
- Alice build concurrent TCP with all its neighbours. Some peers leave and some join, then try new connections to Alice.
- Alice asks all her neighbours for their chunks of file. If Alice has L neighbours, she will obtain L lists of chuncks.
- Two questions Alice should consider: (1) which
chunks should she request first from her neighbors? (2) to which of her neighbors should she
send requested chunks?- (1) answer: rarest first technique.
- (2) answer: trading algorithm.
Reference material:
Book: Computer Networking A Top-Down Approach 7th edition, Jim Kurose & Keith Ross, Addison-Wesley.
Slides: University of Waterloo, ECE 456/656 (Computer Networks), 2020 spring term, Professor Zille Huma Kamal.